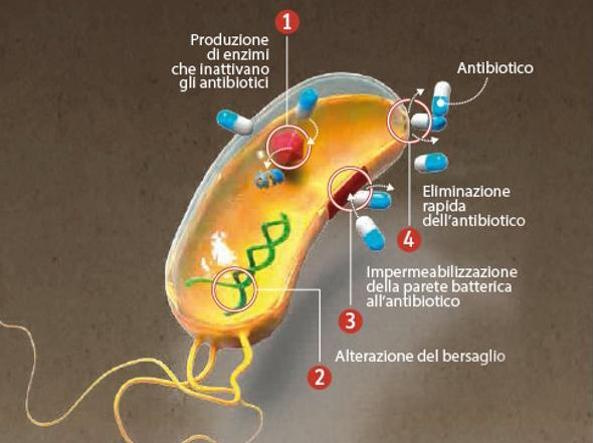
ANTIBIOTICO RESISTENZA
Antibiotic resistance: Latest results from PubMed
-
Antibiotic Resistance Gene Expression in Veterinary Probiotics: Two Sides of the Coin
The rapid proliferation of antimicrobial resistance has emerged as one of the most pressing animal and public health challenges of our time. Probiotics, extensively employed in human and veterinary medicine, are instrumental in maintaining a balanced microbiome and mitigating its disruption during antibiotic therapy. While their numerous benefits are well documented, probiotics also present potential risks, notably the capacity to harbor antimicrobial resistance genes. This genetic reservoir... -
Epitope-Based Vaccines: The Next Generation of Promising Vaccines Against Bacterial Infection
The increasing resistance of bacteria to antibiotics has underscored the need for new drugs or vaccines to prevent bacterial infections. Reducing multidrug resistance is a key objective of the WHO's One Health initiative. Epitopes, the key parts of antigen molecules that determine their specificity, directly stimulate the body to produce specific humoral and/or cellular immune responses. Epitope-based vaccines, which combine dominant epitopes in a rational manner, induce a more efficient and... -
Evaluating HIV drug resistance in the middle East and North Africa and its associated factors: a systematic review
CONCLUSION: This is the first report to provide deep insight into ART resistance patterns in the MENA region among both ART-naïve and ART-experienced PWH. The results revealed a significant occurrence of drug resistance to RTIs, PIs, and INSTIs among both groups. This finding highlights the importance of prescribing the INTIs in native and PWH with resistance to RTIs and/or PIs to increase the chance of response to ART as well as regular monitoring of resistance to ART in MENA countries. This... -
Gut Microbiota in Immuno-Oncology: A Practical Guide for Medical Oncologists With a Focus on Antibiotics Stewardship
The gut microbiota has emerged as a critical determinant of immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) efficacy, resistance, and toxicity. Retrospective and prospective studies profiling the taxonomic composition of intestinal microbes of patients treated with ICI have revealed specific gut microbial signatures associated with response. By contrast, dysbiosis, which can be caused by chronic inflammatory processes (such as cancer) or comedications, is a risk factor of resistance to ICI. Recent large-scale... -
Multi-target mechanisms and potential applications of quercetin in the treatment of acne vulgaris
Acne vulgaris, a prevalent inflammatory dermatosis, afflicts approximately 90% of adolescents globally. Despite the efficacy of conventional therapies, including antibiotics and retinoids, their use is frequently limited by adverse effects and the emergence of drug resistance. Quercetin, a naturally occurring flavonoid, has garnered significant attention owing to its diverse biological activities, encompassing anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antimicrobial, and immunomodulatory properties. This... -
Global trends in antimicrobial resistance of Enterococcus faecium: a systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical isolates
CONCLUSION: Our findings confirm the high antibacterial activity of linezolid against E. faecium isolates. Additionally, our investigation reveals a gradual increase and a concerning upward trend in resistance rates for nearly all agents in recent years. However, the significant reduction in resistance rates for certain antibiotics suggests that these drugs could potentially regain their effectiveness in the future. -
Faecal microbiota transplantation for recurrent Clostridiodes difficile infection & its global regulatory landscape
For recurrent Clostridioides difficile infection (rCDI), faecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) is a known and useful treatment that involves introducing faeces from a healthy individual into the digestive tract of a diseased person. Clostridioides difficile is a substantial global health burden due to its high death rate in elderly populations and its ability to produce colitis and diarrhoea. Despite being used since millennia, FMT has recently become more well-known and two FMT products,... -
The safety and efficacy of non-typeable Haemophilus influenzae and Moraxella catarrhalis vaccine in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
CONCLUSION: Although the NTHi-Mcat/NTHi vaccines were well-tolerated in COPD patients, they did not significantly reduce the risk of exacerbations or mortality. These findings suggest that further research is needed to validate these results and identify potential subgroups that may derive clinical benefit. -
Prevalence of genes encoding carbapenem-resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae recovered from clinical samples in Africa: systematic review and meta-analysis
CONCLUSIONS: The emergence and spread of carbapenemase-encoding genes in K. pneumoniae pose a major threat to public health. Knowledge on the genetic mechanisms of carbapenem resistance is crucial for developing effective strategies to combat these multidrug-resistant infections and reduce their impact on healthcare systems. The carbapenemase genes bla(OXA-48) and bla(NDM-1) were the most prevalent and showed an increasing trend over time. -
An Overview of the Current Approaches in Drug-Resistant Bacterial Removal Within Wastewaters: Can We Move Towards Nanomagnet-Porphyrin Hybrids for Antimicrobial Photodynamic Inactivation (aPDI)
The rise in the occurrence of drug-resistant bacteria within wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) and their dissemination into the ecosystem from the same WWTPs has created a prevalent crisis affecting the integrity of human life and water sources worldwide. Antimicrobial Photodynamic Inactivation (aPDI) can be explored in an effort to address this crisis and preserve natures integrity as it can incorporate environmentally sustainable and cost-effective disinfection strategies within wastewater... -
Selective decontamination of the digestive tract in burn patients: A systematic review with meta-analysis
CONCLUSION: We found that the certainty of evidence is very low about the effects of SDD on patient-important outcomes in burn patients. Extrapolating from the evidence on mechanically ventilated adult ICU patients may be reasonable until more data from RCTs in burn patients emerge. -
Antibiotic resistance genes in Escherichia coli - literature review
Antimicrobial resistance threatens humans and animals worldwide and is recognized as one of the leading global public health issues. Escherichia coli (E. coli) has an unquestionable role in carrying and transmitting antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs), which in many cases are encoded on plasmids or phage, thus creating the potential for horizontal gene transfer. In this literature review, the authors summarize the major antibiotic resistance genes occurring in E. coli bacteria, through the major... -
The use of silver nanoparticles in pigs - An invited review
Silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) have attracted significant interest in veterinary medicine due to their unique properties, including enhanced stability, greater antimicrobial efficacy, and reduced toxicity compared to traditional silver salts. Their applications span various areas of veterinary practice, such as dermatology, wound management, infection prevention, drug delivery, and disinfection. This review explores their use in pigs, highlighting their role as feed additives to prevent diarrhoea,... -
Recent Advances in Steroid Discovery: Structural Diversity and Bioactivity of Marine and Terrestrial Steroids
Steroids have been pivotal in medicine and biology, with research into their therapeutic potential accelerating over the past few decades. This review examines recent steroid discoveries from marine and terrestrial sources, highlighting both novel compounds and those with newly identified biological activities. The structural diversity of these steroids contributes to their wide range of biological activity, including anticancer, antimicrobial, antidiabetic, anti-inflammatory, and... -
The Significance of Fungal Specialized Metabolites in One Health Perspectives
Among the emerging threats in global health, fungal pathogens stand out as some of the most important, causing over 1.6 million deaths annually and destroying a third of all food crops each year, exacerbating food insecurity and economic losses. Climate change further amplifies the threat by enabling pathogenic fungi to survive at mammalian temperatures, increasing risks of zoonotic transmission and antifungal resistance. In this context, interdisciplinary research, particularly the One Health... -
The Role of Gut Microbiome on Glioblastoma Oncogenesis and Malignant Evolution
Glioblastoma (GBM) remains the most aggressive primary brain tumor, with poor survival outcomes and treatment limited to maximal safe surgical resection, chemotherapy with temozolomide, and radiotherapy. While immunotherapy and targeted treatments show promise, therapeutic resistance and disease progression remain major challenges. This is partly due to GBM's classification as a "cold tumor" with low mutational burden and a lack of distinct molecular targets for drug delivery that selectively... -
The Microbiome and Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease
Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) is a condition wherein excessive fat accumulates in the liver, leading to inflammation and potential liver damage. In this narrative review, we evaluate the tissue microbiota, how they arise and their constituent microbes, and the role of the intestinal and hepatic microbiota in MASLD. The history of bacteriophages (phages) and their occurrence in the microbiota, their part in the potential causation of MASLD, and conversely,... -
Short versus longer duration antibiotic treatment for urinary tract infections in companion animals: a systematic review and meta-analysis
CONCLUSION: Based on this data alone, we cannot make conclusions about the efficacy of short compared to long antibiotic durations for treating UTIs in cats and dogs; due to the low numbers of included studies and patients, the confidence intervals for the pooled risk ratio were wide and could be consistent with inferiority or superiority of shorter treatment. Existing evidence supports shorter durations of antibiotics for treating sporadic UTIs in dogs and cats, however this systematic review... -
Listeria monocytogenes and Listeriosis: The Global Enigma
Listeria monocytogenes is an intracellular, Gram-positive, non-spore-forming, non-encapsulated, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, and psychrotrophic food-borne pathogen that causes the infection, listeriosis, thus it attracts great attention following listeriosis outbreaks, which are often associated with high mortality rates. The prevalence of listeriosis is quite low globally; however, the most recent and deadliest outbreak occurred in South Africa, during which 216 persons lost their lives.... -
Role of Lysogenic Phages in the Dissemination of Antibiotic Resistance Genes Applied in the Food Chain
Bacteriophages, first discovered in 1915, have re-emerged as critical players in microbial ecosystems, particularly in food production. Their ability to lysogenize bacterial hosts raises concerns about their role in the horizontal transfer of antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs) and virulence factors, contributing to the global challenge of antimicrobial resistance. Key studies reveal that ARG-carrying phages are prevalent across various stages of the food chain, including soil, vegetables, meat,... -
Artificial intelligence in drug resistance management
This review highlights the application of artificial intelligence (AI), particularly deep learning and machine learning (ML), in managing antimicrobial resistance (AMR). Key findings demonstrate that AI models, such as Naïve Bayes, Decision Trees (DT), Random Forest (RF), Support Vector Machines (SVM), and Artificial Neural Networks (ANN), have significantly advanced the prediction of drug resistance patterns and the identification of novel antibiotics. These algorithms have effectively... -
Exploring the dark side of probiotics to pursue light: Intrinsic and extrinsic risks to be opportunistic pathogens
Probiotics, live microorganisms with multiple health benefits, have gained popularity for their roles in maintaining daily health and treating a variety of diseases. However, they have the potential to be opportunistic pathogens in some conditions. This review delves into the intrinsic and extrinsic risks associated with probiotics. Intrinsic risks involve the production of harmful substances, such as toxins and invasive factors, biofilm formation, bacteria emboli, antibiotic resistance with... -
A systematic review and meta-analysis of antibiotic resistance of foodborne pathogenic bacteria
Antimicrobial drugs are used to treat bacterial pathogens that cause infections in humans and animals. Despite their importance, antimicrobial drugs exhibit inefficiency in treating infections if used irrationally without adherence to standard guidelines. Currently there is a lack of review literatures concerning antimicrobial resistance status in the southern sub Saharan African countries, hence the study is designed for and provides valuable insights into the status and comparison of... -
Bacteriophage therapy: a possible alternative therapy against antibiotic-resistant strains of Klebsiella pneumoniae
Klebsiella pneumoniae is a notorious, Gram-negative pathogen and is a leading cause of healthcare settings and community-acquired infections. This is the commensal of human microbiota and can invade and cause infections in different body parts. The global emergence of antibiotic resistance in K. pneumoniae has become a major challenge in the whole medical community. Alternative paths to treat the infections caused by these MDR pathogens are needed as these bacteria become resistant to... -
Biocides as drivers of antibiotic resistance: A critical review of environmental implications and public health risks
The widespread and indiscriminate use of biocides poses significant threats to global health, socioeconomic development, and environmental sustainability by accelerating antibiotic resistance. Bacterial resistance development is highly complex and influenced significantly by environmental factors. Increased biocide usage in households, agriculture, livestock farming, industrial settings, and hospitals produces persistent chemical residues that pollute soil and aquatic environments. Such... -
Optimizing Cancer Treatment Through Gut Microbiome Modulation
The gut microbiome plays a pivotal role in modulating cancer therapies, including immunotherapy and chemotherapy. Emerging evidence demonstrates its influence on treatment efficacy, immune response, and resistance mechanisms. Specific microbial taxa enhance immune checkpoint inhibitor efficacy, while dysbiosis can contribute to adverse outcomes. Chemotherapy effectiveness is also influenced by microbiome composition, with engineered probiotics and prebiotics offering promising strategies to... -
Colony morphotype variation in Burkholderia: implications for success of applications and therapeutics
The Burkholderia genus includes both environmental and pathogenic isolates known for their phenotypic plasticity and adaptability. Burkholderia spp. are intrinsically resistant to many antibiotics, often requiring prolonged therapies during infection. A key feature of Burkholderia spp. is colony morphotype variation (CMV), which allows for rapid adaptation to environmental changes and influences virulence, antibiotic resistance, and pathogenicity by impacting the expression of key virulence... -
Can we rely on artificial intelligence to guide antimicrobial therapy? A systematic literature review
CONCLUSIONS: AI, particularly machine learning integrated into CDSS, holds promise in enhancing clinical decision-making and improving antimicrobial management. However, large language models currently lack the reliability required for complex clinical applications. The indispensable role of infectious disease specialists remains critical for ensuring accurate, personalized, and safe treatment strategies. Rigorous validation and regular updates are essential before the successful integration of... -
Navigating Antimicrobials and Combating Antimicrobial Resistance: Challenges, Impacts, and Strategies for Global Action
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is one of the biggest problems facing the scientific and medical communities. According to WHO, this growing issue might make once-effective antibiotics obsolete and pose a substantial risk to public health. Estimates indicate that multimillion deaths were either directly or indirectly caused by AMR, making it one of the most substantial risks to public health and development in the world. The issue of AMR is primarily caused by healthcare workers' excessive and... -
Recombinant Antimicrobial Peptides (rAMPs); Potential Applications in Medicine and Veterinary Medicine: A Review
Antibiotic resistance has become a major public health concern worldwide. Treatment of humans and animals is becoming increasingly challenging due to antibiotic resistance. Antibiotic-resistant bacteria can be transmitted from animals to humans by several routes, including direct contact, contaminated food or water, or environmental exposure. Various factors contribute to the rising problem, such as the widespread and indiscriminate exploitation of antimicrobials in both human and animal... -
Clarithromycin-resistant Helicobacter pylori in Africa: a systematic review and meta-analysis
CONCLUSION: To enhance the accuracy and validity of surveillance data for H. pylori in Africa, there is an urgent need for implementing standardized microbiological methods for resistance detection. The prevalence of CRHp reported in this study was very similar to the overall global prevalence and there is a need for more representative studies on CRHp in Africa. While waiting for this, the treatment of H. pylori infections must be based on the guidelines of the AHMSG first Lagos consensus. -
A tympanitis-related brain abscess caused by Helcococcus kunzii in China: a case report and literature review
CONCLUSIONS: This case underscores the increasing acknowledgment of H. kunzii as a notable pathogen in invasive intracranial infections. It is imperative for clinicians to consider H. kunzii in the differential diagnosis of patients presenting with intracranial infections, especially those with a history of tympanitis, to ensure prompt and effective management. The utilization of MS and molecular techniques should be prioritized for the accurate identification of these anaerobic bacteria. -
Antimicrobial resistance pattern of Acinetobacter baumannii clinical isolate in Ethiopia. A systematic review and meta-analysis
CONCLUSION: This systematic review underscores the alarming rise of antimicrobial resistance in A. baumannii, particularly against carbapenems. The findings highlight a high prevalence of MDR A. baumannii and widespread extended-spectrum beta-lactamase production, with notable regional variations in resistance patterns. These high resistance rates reinforce A. baumannii as a critical global health threat, necessitating urgent interventions such as enhanced antimicrobial stewardship programs,... -
Antifungal Resistance in Non-fumigatus Aspergillus Species
This review provides an in-depth exploration of antifungal resistance in non-fumigatus Aspergillus species, mainly focusing on acquired resistance. The available data have been compiled and sometimes re-analysed. It highlights the increasing prevalence of resistance in non-fumigatus species belonging to Flavi, Terrei, Nigri, and Nidulantes Aspergillus sections, offering a detailed analysis of resistance detection methods and the global distribution of resistant strains. The review also... -
Antibiotic resistance in hospital wastewater in West Africa: a systematic review and meta-analysis
CONCLUSION: This systematic review highlights significant findings of high levels of ARGs and ARBs of public health concern in HWW in West Africa. This highlights the need to improve upon the monitoring of antibiotic resistance and treatment of HWW in West Africa. -
Prevalence, antibiogram, and risk factors of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) asymptomatic carriage in Africa: a systematic review and meta-analysis
CONCLUSION: MRSA colonization is a significant public health challenge in Africa, particularly among healthcare workers and hospitalized patients. Implementing targeted interventions for these high-risk groups can effectively reduce MRSA transmission and overall infection burden. Continuous monitoring is essential, especially given the resistance to mupirocin, a key antibiotic used for MRSA decolonization. -
Antimicrobial peptides: a promising frontier to combat antibiotic resistant pathogens
Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) are varied naturally occurring compounds that are crucial to the innate immune system among several organisms. These peptides are effective against various bacteria, viruses, fungus, and cancer cells. Alternative therapeutic options are becoming more important as drug-resistant diseases become a global concern nowadays. AMPs unique modes of action and benefits over traditional antibiotics make them potential candidates for improving drug-resistant disease treatment.... -
Candida albicans: the current status regarding vaginal infections
Vaginal infections caused by Candida albicans are a significant global health concern due to their recurrence and negative impact on quality of life. This review examines the pathogenesis of C. albicans infections, emphasizing critical virulence factors such as biofilm formation, adherence, and phenotypic switching. Risk factors include immune system suppression, antibiotic use, and hormonal changes, all of which can lead to fungal overgrowth and infection. Current prevention and/or treatment... -
Asymptomatic Leukocytospermia and Assisted Reproductive Technology Outcomes: Reason for concern?
Leukocytospermia, defined as ≥1×10⁶ white blood cells (WBC)/ml of semen, is a condition frequently observed in infertile men. While symptomatic leukocytospermia is often associated with genital tract infections and managed accordingly, the clinical significance of asymptomatic leukocytospermia remains uncertain-particularly in the setting of Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART). Seminal leukocytes, primarily neutrophils, play a physiological role in immune surveillance and tissue homeostasis.... -
The oncobiome; what, so what, now what?
Microbial communities inhabiting various body sites play critical roles in the initiation, progression, and treatment of cancer. The gut microbiota, a highly diverse microbial ecosystem, interacts with immune cells to modulate inflammation and immune surveillance, influencing cancer risk and therapeutic outcomes. Local tissue microbiota may impact the transition from premalignant states to malignancy. Characterization of the intratumoral microbiota increasingly reveals distinct microbiomes that... -
Exploring the diversity and antimicrobial potential of actinomycetes isolated from different environments in Saudi Arabia: a systematic review
The increasing prevalence of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) presents a significant global health challenge, underscoring the urgent need for novel antimicrobial agents. Actinomycetes, particularly Streptomyces species, are well known for synthesizing bioactive compounds with antibacterial, antifungal, and antiviral properties. This review explores the diversity and antimicrobial potential of actinomycetes from Saudi Arabia's unique ecosystems, including terrestrial (soil, rhizosphere), aquatic... -
A review on the green synthesis of metal (Ag, Cu, and Au) and metal oxide (ZnO, MgO, Co3O4, and TiO2) nanoparticles using plant extracts for developing antimicrobial properties
Green synthesis (GS) is a vital method for producing metal nanoparticles with antimicrobial properties. Unlike traditional methods, green synthesis utilizes natural substances, such as plant extracts, microorganisms, etc., to create nanoparticles. This eco-friendly approach results in non-toxic and biocompatible nanoparticles with superior antimicrobial activity. This paper reviews the prospects of green synthesis of metal nanoparticles of silver (Ag), copper (Cu), gold (Au) and metal oxide... -
Global initiatives to phase-out colistin use in food-producing animals
CONCLUSIONS: The testimonies of 29 countries representing global initiatives to phase-out colistin use in animal production. -
Potential of the livestock industry environment as a reservoir for spreading antimicrobial resistance
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) in bacteria is a global issue requiring serious attention and management. The indiscriminate use of antibiotics in livestock for growth promotion, disease prevention, and treatment has led to the dissemination of AMR bacteria and resistance genes into the environment. In addition, unethical antibiotic sales without prescriptions, poor sanitation, and improper disposal cause significant amounts of antibiotics used in livestock to enter the environment, causing the... -
Antimicrobial activity of cranberry juice (Vaccinium macrocarpon L.) ethanol extract against uropathogenic bacteria
CONCLUSION: The results show that the ethanol extract of CJ has potent antibacterial activity against uropathogenic bacteria, suggesting a possible role for CJ ethanol extract in treating UTIs when combined with recently emerging facts about increasing antibiotic resistance. -
Role of phage therapy in acute gastroenteritis
The gut ecosystem, comprising the gut microbiota and its interactions, plays a crucial role in human health and disease. This complex ecosystem involves a diverse array of microorganisms such as viruses, fungi, and bacteria, collectively known as the gut microbiota. These microorganisms contribute to various functions, including nutrient metabolism and immune modulation, thereby impacting human health. Dysbiosis, or an imbalance in the gut microbiota, has been associated with the pathogenesis of... -
Catheter associated urinary tract infection: 2024 update and intersociety recommendations
Representatives of the Argentine Society of Infectious Diseases (SADI) and the Argentine Society of Intensive Therapy (SATI) issued the present recommendations on diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of catheter associated urinary tract infection (CA-UTI). Articles published during 2018-2024 were analyzed in the light of experts' opinion and local data. This document aims to offer basic strategies to optimize the diagnosis based on clinical and microbiological criteria, provide guidance in... -
Exploring the role of strontium-based nanoparticles in modulating bone regeneration and antimicrobial resistance: a public health perspective
Strontium-based nanoparticles (SrNPs) have emerged as a versatile and promising class of nanomaterials with a wide range of potential applications in healthcare, particularly in the fields of bone regeneration and combating antimicrobial resistance (AMR). Recent research has highlighted the unique properties of SrNPs, including their ability to promote osteogenesis, enhance bone healing, and exhibit strong antimicrobial activity against multidrug-resistant pathogens. These attributes position... -
Leveraging strain competition to address antimicrobial resistance with microbiota therapies
The enteric microbiota is an established reservoir for multidrug-resistant organisms that present urgent clinical and public health threats. Observational data and small interventional studies suggest that microbiome interventions, such as fecal microbiota products and characterized live biotherapeutic bacterial strains, could be an effective antibiotic-sparing prevention approach to address these threats. However, bacterial colonization is a complex ecological phenomenon that remains... -
Regulation, structure, and activity of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa MexXY efflux system
The current crisis in bacterial antibiotic resistance can be attributed to the overuse (or misuse) of these essential medicines in healthcare and agriculture, coupled with the slowed progression of new drug development. In the versatile, opportunistic pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa, the Resistance-Nodulation-Division (RND) efflux pump MexXY plays critical roles in both cell physiology and the acquisition of multidrug resistance. The mexXY operon is not constitutively expressed, but this process... -
Assessing the impact of probiotics on immunotherapy effectiveness and antibiotic-mediated resistance in cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis
CONCLUSIONS: The meta-analysis findings suggest that probiotics can effectively extend the survival of cancer treated with ICIs. In NSCLC, probiotics appear to mitigate the negative impact of antibiotics on immunotherapy effectiveness, which has profound clinical significance. Nevertheless, additional large-scale, high-quality randomized controlled trials are necessary to further validate these findings. -
Therapeutic Outcomes in Patients With Trichophyton indotineae: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Individual Patient Data
CONCLUSIONS: The effective management of T. indotineae infections is essential, given the significant challenges posed by antifungal resistance. -
Metabolic state-driven nutrient-based approach to combat bacterial antibiotic resistance
To combat antibiotic resistance, one innovative approach, known as the metabolic state-driven approach, exploits the fact that exogenous nutrient metabolites can stimulate uptake of antibiotics. The most effective nutrient metabolites are identified by comparing metabolic states between antibiotic-sensitive and -resistant bacteria. When bacteria are exposed to the specific nutrient metabolites, they undergo a form of metabolic reprogramming. This review summarizes the recent progress on the... -
Diagnostic accuracy of nanopore sequencing for detecting Mycobacterium tuberculosis and drug-resistant strains: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Tuberculosis (TB), caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB) infection, remains a significant public health threat. The timeliness, portability, and capacity of nanopore sequencing for diagnostics can aid in early detection and drug susceptibility testing (DST), which is crucial for effective TB control. This study synthesized current evidence on the diagnostic accuracy of the nanopore sequencing technology in detecting MTB and its DST profile. A comprehensive literature search in PubMed,... -
How Should Cytomegalovirus Infection Be Managed in Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant Recipients? A Clinical Grand Round
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) is a significant concern for patients with allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (allo-HCT). CMV management differs between institutions due to the lack of local guidelines. Here, we describe a case of refractory/resistant CMV infection treated using our institution's CMV management protocol. A 59-year-old woman who underwent allo-HCT was treated for CMV reactivation. Despite 3 months of valganciclovir administration, serum CMV level surged. CMV gene mutation test... -
Recent advances in nanomaterials and their mechanisms for infected wounds management
Wounds infected by bacteria pose a considerable challenge in the field of healthcare, particularly with the increasing prevalence of antibiotic-resistant pathogens. Traditional antibiotics often fail to achieve effective results due to limited penetration, resistance development, and inadequate local concentration at wound sites. These limitations necessitate the exploration of alternative strategies that can overcome the drawbacks of conventional therapies. Nanomaterials have emerged as a... -
Global prevalence of macrolide-resistant Staphylococcus spp.: a comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis
CONCLUSION: This study emphasizes the high prevalence of macrolide resistance in Staphylococcus spp. and its notable regional variation. These findings highlight the necessity for standardized methodologies and global surveillance to manage macrolide resistance effectively. Controlling antibiotic resistance should prioritize enhancing public health measures and updating treatment guidelines. -
Intervention strategies for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus control in pig farming: a comprehensive review
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) poses a serious public health threat due to its zoonotic potential and resistance to several antibiotic classes. Pig farming is recognized as a key reservoir for livestock-associated MRSA, necessitating effective intervention strategies to mitigate its prevalence. The objective of this narrative review was to summarize the current knowledge on the approaches to control MRSA on pig farms. The review process involved a comprehensive search across... -
Reserve antibiotics: overcoming limitations of evidence generated from regulatory approval trials
New antibiotics active against multidrug resistant bacteria (MDR-B) are licensed by regulatory agencies based on pivotal trials that serve the primary purpose of obtaining marketing-authorization. There is increasing concern that they do not offer guidance on how to best use new antibiotics, in which population, and to what extent they overcome existing resistance. We reviewed the literature for pre-approval studies (phase 2 and 3 randomized controlled trials) and post-approval studies... -
Telemedicine interventions for improving antibiotic stewardship and prescribing: A systematic review
The global antibiotic resistance crisis necessitates optimized stewardship programs, with telemedicine emerging as a promising delivery strategy. This systematic review evaluated the effectiveness of telemedicine interventions in improving antibiotic stewardship across clinical settings. Following Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines, we systematically searched seven databases from January 2010 to July 2024. Two independent reviewers assessed... -
A systematic review of the avian antibody (IgY) therapeutic effects on human bacterial infections over the decade
The overuse of antibiotics worldwide, especially during the Coronavirus pandemic, has raised concerns about the rise of antibiotic resistance and its side effects. Immunoglobulin Y, a natural protein that specifically targets foreign antigens, holds promise as a potential therapeutic option, particularly for individuals with sensitive immune systems. Despite numerous studies on IgY, the optimal administration method, effective dose, target antigen, and potential side effects of this antibody... -
Prevalence of the Antibiotic Resistance of Salmonella typhi and Salmonella paratyphi in Pakistan: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
CONCLUSIONS: The findings revealed the alarming prevalence of antibiotic-resistant Salmonella in Pakistan and the need for updated treatment guidelines. Public health strategies must focus on improving antibiotic use and developing alternative treatment options to mitigate the rising threat of resistant Salmonella strains. Continued research, policy intervention, and national and international cooperation are essential to safeguard public health and ensure effective management of enteric fever. -
Beyond antibiotics: exploring multifaceted approaches to combat bacterial resistance in the modern era: a comprehensive review
Antibiotics represent one of the most significant medical breakthroughs of the twentieth century, playing a critical role in combating bacterial infections. However, the rapid emergence of antibiotic resistance has become a major global health crisis, significantly complicating treatment protocols. This paper provides a narrative review of the current state of antibiotic resistance, synthesizing findings from primary research and comprehensive review articles to examine the various mechanisms... -
Reinvigorating AMR resilience: leveraging CRISPR-Cas technology potentials to combat the 2024 WHO bacterial priority pathogens for enhanced global health security-a systematic review
CONCLUSIONS: CRISPR-Cas technology has the potential to address AMR across priority WHO pathogens. While promising, challenges in optimizing in vivo delivery, mitigating potential resistance, and navigating ethical-regulatory barriers must be addressed to facilitate clinical translation. -
Dominance of antimicrobial resistance bacteria and risk factors of bacteriuria infection among pregnant women in East Africa: implications for public health
CONCLUSIONS: This analysis reveals a significant prevalence of bacterial infections, particularly Escherichia coli, among pregnant women in East Africa, with antimicrobial resistance (AMR) complicating treatment. The study identified several key risk factors, including antibiotic use, smoking, poor sanitation, diabetes, and age over 30, which are associated with higher rates of infection. While these findings emphasize the need for further research, the results suggest that routine bacterial... -
Factors influencing vaccine hesitancy toward non-covid vaccines in South Asia: a systematic review
Declared as one of the ten most pressing threats to global health in 2019, the complexity around vaccine acceptance and hesitancy has once again gained great momentum following the COVID-19 pandemic. Lack of vaccine acceptance may endanger the mission of improving vaccine uptake globally to tackle pandemics, reduce morbidity and mortality of preventable diseases and to prevent antibiotic resistance worldwide. Countries of the global south, including South Asian Association for Regional... -
Recalcitrant dermatophytosis
In recent years, we have witnessed a rise in antifungal resistance, notably due to the emergence of Trichophyton indotineae, which is highly resistant to terbinafine. In Denmark, Trichophyton rubrum remains the most frequent causative agent. Antifungal susceptibility testing when resistance is suspected is critical for guiding treatment decisions. To prevent recalcitrant dermatophytosis from becoming endemic, it is essential to implement surveillance programs, screen close contacts, and restrict... -
Nanomedicine approaches to enhance the effectiveness of meropenem: a strategy to tackle antimicrobial resistance
Meropenem, a carbapenem typically reserved for treating severe infections, has encountered resistance from certain bacteria, including multidrug-resistant (MDR) strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa (P. aeruginosa) and Klebsiella pneumonia (K. pneumonia). Nanoparticles (NPs) have emerged as a promising strategy to combat drug-resistant bacteria. By targeting specific biosynthetic and enzymatic pathways and penetrating bacterial membranes, NPs can function as antibiotic delivery systems... -
Harnessing the human gut microbiota: an emerging frontier in combatting multidrug-resistant bacteria
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) has become a major and escalating global health threat, undermining the effectiveness of current antibiotic and antimicrobial therapies. The rise of multidrug-resistant bacteria has led to increasingly difficult-to-treat infections, resulting in higher morbidity, mortality, and healthcare costs. Tackling this crisis requires the development of novel antimicrobial agents, optimization of current therapeutic strategies, and global initiatives in infection... -
Text mining and topic modeling insights on fish welfare and antimicrobial use in aquaculture
Antimicrobial use (AMU) and antibiotic resistance (AR) in aquaculture present growing concerns for public health. Furthermore, there exists a correlation between fishes' welfare and AMU. This systematic review aims to analyze the scientific literature on fishes' welfare and AMU/AR over the last 32 years, identifing the main research topics, and the fields where investigation has been imitated. A comprehensive search was conducted using Scopus, employing specific keywords related to AMU/AR and... -
A Comprehensive Overview of Klebsiella Pneumoniae: Resistance Dynamics, Clinical Manifestations, and Therapeutic Options
Klebsiella pneumoniae (Kp) is a notable pathogen responsible for various infections. The emergence of hypervirulent and carbapenem-resistant strains has raised global concern. Many novel approaches were developed to combat the current severe situation of antibiotic resistance, and clinical guidelines have also provided corresponding recommendations. This review highlights the critical aspects of Kp, including classification, virulence factors, systemic dissemination, drug resistance progression... -
Microbiota modulation for infectious complications following allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in pediatric hematological malignancies
The intervention of microbiota modulation in the treatment of infection complications after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in pediatric patients with hematological malignancies has shown potential benefits. Through the use of probiotics, prebiotics, synbiotics, and fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT), these interventions modulate the gut microbiota and enhance immune function to prevent and treat infections. They have been shown to reduce the incidence of diarrhea and... -
Quorum Sensing: Not Just a Bridge Between Bacteria
The study of quorum sensing (QS) has gained critical importance, offering insights into bacterial and microorganism communication. QS, regulated by autoinducers, synchronizes collective bacterial behaviors across diverse chemical signals and target genes. This review highlights innovative approaches to regulating QS, emphasizing the potential of quorum quenching and QS inhibitors to mitigate bacterial pathogenicity. These strategies have shown promise in aquaculture and plant resistance,... -
Prevalence of colistin-resistant Enterobacteriaceae isolated from clinical samples in Africa: a systematic review and meta-analysis
CONCLUSIONS: Colistin resistance in Enterobacteriaceae is notably high in Africa, with significant variation across countries. This underscores the urgent need for effective antimicrobial stewardship, improved surveillance, and the development of new antibiotics. -
Evaluation of antimicrobial resistance surveillance data sources in primary care setting: a scoping review
CONCLUSION: This analysis highlights the need for user-friendly, real-time, and easily accessible data visualization platforms to improve AMR surveillance and AMS in primary care. Addressing data accessibility and providing training and education are crucial elements. Standardising data and utilizing digital technologies can improve decision-making and antibiotic prescribing. These elements must be incorporated into a consistent and adaptive plan for effective AMS interventions and public health... -
Enhancing antimicrobial resistance surveillance and research: a systematic scoping review on the possibilities, yield and methods of data linkage studies
CONCLUSION: This systematic scoping review showed that AMR data linkage studies are increasingly performed. They have potential to gain a more comprehensive understanding of AMR dynamics by generating hypotheses, assisting in optimisation of surveillance, and interpretation of data in the context of guideline/policy development. To increase the added value of data linkage, more studies should be performed to improve knowledge on methodological approaches, data access, data management, and... -
Enterococcus: Understanding Their Resistance Mechanisms, Therapeutic Challenges, and Emerging Threats
The Enterococcus species originates as non-harmful bacteria indigenous to human intestines but has transformed into severe hospital-acquired pathogens due to antimicrobial resistance (AMR). The clinical species Enterococcus faecalis and Enterococcus faecium create the most relevant infections because they appear in urinary tract infections, bloodstream infections, endocarditis, and wound infections. Enterococcus species demonstrate multiple antibiotic class resistance and resistance determinant... -
Rare or Unusual Non-Fermenting Gram-Negative Bacteria: Therapeutic Approach and Antibiotic Treatment Options
Non-fermenting Gram-negative bacteria (NFGNB) are a heterogeneous group of opportunistic pathogens increasingly associated with healthcare-associated infections. While Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Acinetobacter baumannii, and Stenotrophomonas maltophilia are well known, rarer species such as Burkholderia cepacia complex, Achromobacter spp., Chryseobacterium spp., Elizabethkingia spp., Ralstonia spp., and others pose emerging therapeutic challenges. Their intrinsic and acquired resistance mechanisms... -
Antibiotics and Opportunities of Their Alternatives in Pig Production: Mechanisms Through Modulating Intestinal Microbiota on Intestinal Health and Growth
Antibiotics at subtherapeutic levels have been used in pig diets as antimicrobial growth promoters. However, concerns about antibiotic resistance have increased the demand for alternatives to these antimicrobial growth promoters. This review paper explores the mechanisms through which antimicrobial growth promoters and their alternatives exert their antimicrobial effects. Additionally, this systemic review also covers how modulation of intestinal microbiota by antimicrobial growth promoters or... -
Metagenomics as a Transformative Tool for Antibiotic Resistance Surveillance: Highlighting the Impact of Mobile Genetic Elements with a Focus on the Complex Role of Phages
Extensive use of antibiotics in human healthcare as well as in agricultural and environmental settings has led to the emergence and spread of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, rendering many infections increasingly difficult to treat. Coupled with the limited development of new antibiotics, the rise of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) has caused a major health crisis worldwide, which calls for immediate action. Strengthening AMR surveillance systems is, therefore, crucial to global and national... -
Phenolic Compounds from Pyrus communis Residues: Mechanisms of Antibacterial Action and Therapeutic Applications
CONCLUSIONS: While P. communis phenolics show promise as natural antibacterial agents, future research should address bioavailability, extraction standardization, and safe formulation strategies. Investigating their synergy with conventional antibiotics and improving stability for cosmetic applications are key steps toward their practical use. In vivo and clinical studies are crucial to validating their therapeutic potential and ensuring regulatory approval. -
Exploring the Impact of Chemotherapy on the Emergence of Antibiotic Resistance in the Gut Microbiota of Colorectal Cancer Patients
With nearly half of colorectal cancer (CRC) patients diagnosed at advanced stages where surgery alone is insufficient, chemotherapy remains a cornerstone for this cancer treatment. To prevent infections and improve outcomes, antibiotics are often co-administered. However, chemotherapeutic interactions with the gut microbiota cause significant non-selective toxicity, affecting not only tumor and normal epithelial cells but also the gut microbiota. This toxicity triggers the bacterial SOS response... -
Honey as a Natural Antimicrobial
Honey, a natural product with a rich history of medicinal use, has gained increasing recognition for its potent antimicrobial properties, particularly against antibiotic-resistant pathogens. This review focuses on the antimicrobial mechanisms of honey, including its efficacy against resistant bacteria, such as Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. The antimicrobial action of honey is multifactorial, involving hydrogen peroxide production, phenolic compounds,... -
Recent Advances in Biofilm Control Technologies for the Food Industry
Biofilms remain a major challenge in the food industry due to the increased resistance of foodborne pathogens to antimicrobial agents and food processing stresses, leading to food contamination and significant health risks. Their resistance to preservation techniques, antimicrobial treatments, and processing conditions increases concerns regarding food safety. This review discusses recent developments in physical, chemical, and surface modification strategies to control and remove biofilms in... -
The Invisible Threat of Antibiotic Resistance in Food
The continued and improper use of antibiotics has resulted in the emergence of antibiotic resistance (AR). The dissemination of antibiotic-resistant microorganisms occurs via a multitude of pathways, including the food supply. The failure to comply with the regulatory withdrawal period associated with the treatment of domestic animals or the illicit use of antibiotics as growth promoters has contributed to the proliferation of antibiotic-resistant bacteria in meat and dairy products. It was... -
Acquired Bacterial Resistance to Antibiotics and Resistance Genes: From Past to Future
The discovery, commercialization, and regular administration of antimicrobial agents have revolutionized the therapeutic paradigm, making it possible to treat previously untreatable and fatal infections. However, the excessive use of antibiotics has led to develop resistance soon after their use in clinical practice, to the point of becoming a global emergency. The mechanisms of bacterial resistance to antibiotics are manifold, including mechanisms of destruction or inactivation, target site... -
A Comprehensive Overview of Antibacterial Agents for Combating Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria: The Current Landscape, Development, Future Opportunities, and Challenges
Background/Objectives: Antimicrobial resistance poses a major public health challenge. The World Health Organization has identified 15 priority pathogens that require prompt development of new antibiotics. This review systematically evaluates the antibacterial resistance of the most significant bacterial pathogens, currently available treatment options, as well as complementary approaches for the management of infections caused by the most challenging multidrug-resistant (MDR) bacteria. For... -
Pharmacological treatment for metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease and related disorders: Current and emerging therapeutic options
Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD; formerly known as nonalcoholic fatty liver disease) is a chronic liver disease affecting over a billion individuals worldwide. MASLD can gradually develop into more severe liver pathologies, including metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH), cirrhosis, and liver malignancy. Notably, although being a global health problem, there are very limited therapeutic options against MASLD and its related diseases. While a... -
Evolving patterns of macrolide and fluoroquinolone resistance in Mycoplasma genitalium: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis
BACKGROUND: Over the past 5 years, since publication of the initial review, studies have provided additional data on macrolide and fluoroquinolone resistance in Mycoplasma genitalium, including data from regions previously lacking this information. We aimed to provide contemporary estimates of macrolide and fluoroquinolone resistance in M genitalium to inform national, regional, and global treatment guidelines. -
Systematic review of antibacterial potential in calcium oxide and silicon oxide nanoparticles for clinical and environmental infection control
A substantial threat to worldwide health, the proliferation of antibiotic-resistant bacteria compels researchers to seek innovative antibacterial substances. This systematic review assesses the role of nanoparticles, particularly Calcium oxide and Silicon oxide nanoparticles, in infection control. The article examines the mechanisms by which these nanoparticles act against various bacteria and evaluates their potential as novel agents in infection control strategies. A systematic literature... -
Vatairea Genus as a Potential Therapeutic Agent-A Comprehensive Review of Ethnobotanical, Phytochemical, and Pharmacological Properties
The Vatairea genus (Fabaceae family) is widespread in the Amazon rainforest. Some species of this genus are known for their ethnobotanical significance and biological potential. The present study explores the pharmacological and promising therapeutic activities, ethnobotanical profile, and phytochemical prospection of Vatairea sp., a monophyletic group of flowering plants, which includes economically and culturally important genera due to their diverse uses, including medicinal applications. V.... -
Green Tea: A Novel Perspective on the Traditional Plant's Potential in Managing Periodontal Diseases
Green tea (Camellia sinensis) exhibits significant potential in oral health due to its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antimicrobial properties. This review explores its role in managing periodontal disease, a common condition characterized by inflammation, microbial imbalances, and tissue destruction. The primary bioactive components, particularly epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG), contribute to green tea's therapeutic effects by inhibiting bacterial adhesion, modulating inflammatory... -
Combating Antibiotic Resistance: Mechanisms, Multidrug-Resistant Pathogens, and Novel Therapeutic Approaches: An Updated Review
The escalating global health crisis of antibiotic resistance, driven by the rapid emergence of multidrug-resistant (MDR) bacterial pathogens, necessitates urgent and innovative countermeasures. This review comprehensively examines the diverse mechanisms employed by bacteria to evade antibiotic action, including alterations in cell membrane permeability, efflux pump overexpression, biofilm formation, target site modifications, and the enzymatic degradation of antibiotics. Specific focus is given... -
Small-Molecule Probes: Recent Progress in the Rapid Detection of Carbapenemase-Producing Bacteria
As the last resort and one of the most crucial antibiotics for multidrug-resistant bacteria, carbapenem is considered the best hope for treating bacterial infections. However, the prompt emergence of carbapenemase-producing bacteria (CPB) poses a striking global health threat. Thus, accurate and rapid methods for the detection of carbapenemase are being requested to guide precise diagnosis, appropriate treatment strategies, and antibiotic stewardship. Although genotypic, phenotypic, and... -
The Potential Impact of Antibiotic Exposure on the Microbiome and Human Health
Antibiotics are a cornerstone of modern medicine, saving countless lives. However, their widespread use presents two major challenges. First, antibiotic-induced changes in the microbiome can disrupt immune function, increasing the susceptibility to diseases associated with these alterations. Second, prolonged antibiotic use fosters the proliferation of antibiotic resistance genes, leading to the emergence of resistant strains and threatening our ability to control infections. These challenges... -
Streptococcus salivarius and Ligilactobacillus salivarius: Paragons of Probiotic Potential and Reservoirs of Novel Antimicrobials
This review highlights several basic problems associated with bacterial drug resistance, including the decreasing efficacy of commercially available antimicrobials as well as the related problem of microbiome irregularity and dysbiosis. The article explains that this present situation is addressable through LAB species, such as Streptococcus salivarius and Ligilactobacillus salivarius, which are well established synthesizers of both broad- and narrow-spectrum antimicrobials. The sheer number of... -
Pneumonia: Recent Updates on Diagnosis and Treatment
Pneumonia remains a leading cause of mortality internationally, making it an intense area of study for new tools for diagnosis and treatment. In this review, we evaluate the potential of recently emerging syndromic panels in promoting rapid diagnosis and improved antibiotic stewardship. We will also examine emerging treatments, including new antibiotics in a world of worsening antimicrobial resistance, in addition to new methods of delivery and non-antibiotic paths of treatment. -
Evolution of beta-Lactam Antibiotic Resistance in Proteus Species: From Extended-Spectrum and Plasmid-Mediated AmpC beta-Lactamases to Carbapenemases
The management of infectious diseases has proven to be a daunting task for clinicians worldwide, and the rapid development of antibiotic resistance among Gram-negative bacteria is making it even more challenging. The first-line therapy is empirical, and it most often comprises β-lactam antibiotics. Among Gram-negative bacteria, Proteus mirabilis, an important community and hospital pathogen associated primarily with urinary tract and wound infection, holds a special place. This review's aim was... -
Biofilm-Associated Amyloid Proteins Linked with the Progression of Neurodegenerative Diseases
Biofilm-associated amyloid proteins have emerged as significant contributors to the progression of neurodegenerative diseases, representing a complex intersection of microorganisms and human health. The cross-beta sheet structure characteristic of amyloids produced by gut-colonizing bacteria remains intact, crucial for the resilience of biofilms. These amyloids exacerbate neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's by cross-seeding human amyloidogenic proteins like... -
Flavonoids as Promising Natural Compounds for Combating Bacterial Infections
The increasing emergence and dissemination of multidrug-resistant (MDR) bacterial pathogens have intensified the need for new antibiotics and alternative therapeutic strategies. Flavonoids, a diverse group of bioactive natural compounds found in plants, have shown significant promise as antibacterial agents. Flavonoids inhibit bacterial growth through various mechanisms, including disruption of cell wall synthesis, prevention of biofilm formation, disruption of cell membrane integrity, and...



